RMI Layers RMI Layers
RMI system is organized as a four-layer model. Each layer performs
some specific functions like establishing the connection, marshaling
of parameters, etc. Each layer insulates the layers above it from some
details.
The four layers are:
 Application
Layer Application
Layer
 Proxy
Layer Proxy
Layer
 Remote
Reference Remote
Reference
 Transport
Layer Transport
Layer
 Figure 2.3 Figure 2.3
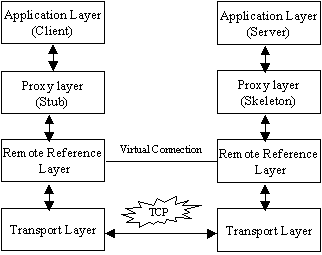
 Application layer Application layer
The application layer is the actual implementation of the client and
server application. Here, the high level calls are made to access and
export remote objects. The class java.rmi.UnicastRemoteObject
provides support for creating and exporting remote objects. Objects
that require remote behavior should extend UnicastRemoteObject,
or if the object extends any other class then the object must be exported
explicitly by calling the UnicastRemoteObject(s)
exportObject() methods. The server creates remote objects and
registers them with the registry service. A client gets a reference
to a remote object by looking up in the server's registry. After an
initial contact with the server, references to remote objects can be
obtained as a return value in a method call.
 Proxy Layer Proxy Layer
To understand how RMI works, we must understand the role of stubs &
skeletons. A stub acts as a client(s) local representative for
remote object. The client invokes a method on the local stub. The stub
is responsible for calling the method on the remote object.
Responsibilities of stub are:
- It connects to the remote JVM.
- It serializes any arguments to a remote method.
- It reads the values returned by a remote method.
- It returns the value to the client.
The skeleton acts as a server side proxy of the remote
objects.
Responsibilities of skeleton are:
- It reads the parameters for the remote object.
- It locates the object to be called.
- It invokes the desired method on remote object.
- It transmits the result to the stub.
|
Skeletons
are not needed for the JDK 1.2 stub protocol. The RMI library
is responsible for handling marshalling and unmarshalling.
|
|