|
|
Process SpecificationThe overall description of the AMS process requires understanding
the physical location of the program and application being stored
in the physical machines. The description is as follows:
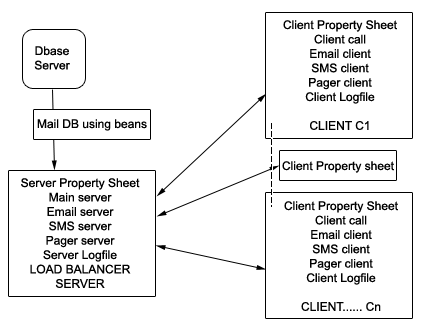
The AMS is designed as the integration of SMS, Pager, & e-mail services. The flow of invoking of their servers and their respective clients is very important. We can define the overall flow of entire process, i.e., which client and server application will get invoked from where and how. There are three services SMS, Pager, and email. Every service has its server application like SMS server, email server, and pager server with its respective client application like SMS client, Email client, & pager client. When we have to use particular service then the server application of the respective service will communicate to the corresponding client (through a socket connection at a particular port number). The servers & clients have their own property sheets through which they get the parameters about the starting of server & client application. The server of particular service gets invoked by reading the attributes from the server property sheet. The server property sheet has attributes like:
Now the corresponding servers of services will get started at Load balancer server. Corresponding to the server application the client application will also be started. This process gets activated by class file called "client call". This will activate/invoke which services you want to start from a particular client. This activation is also done by reading the client property sheet. This sheet is usually different from machine to machine. This is usually one client property sheet per one physical client machine. It has the information like:
The value of particular key is taken from the client property sheet using the property resource bundle. We have defined the option for which services to start from which machine because the client property sheet is different for different client machines. On client machine those applications will get started which have their status "ON" in client property sheet. The applications that have status "OFF" in client property sheet will not be able to get activated. Now the server & the client application get invoked & they can communicate with each other through socket connection. The working and behaviors of the clients and servers is same, it depends on which service is running. For simplicity we are explaining the generalized process of server & client. The database server connectivity part is being implemented in a different application named as "MailDB". The methods used by this application for storing/retrieving from the database are being implemented in bean class. This database application is segregated because all the servers and clients call the "MailDB" program. In fact the database connection is done using a particular bean which creates the connection only once. Every server application will call this "MailDB" program in its class constructor. Now the server application of different services has common methods defined because the application are being extended from the thread class & implemented by the load balancer server.
|
UNIVERSAL
TEACHER PUBLICATIONS
Web: universalteacherpublications.com,
universalteacher.com,
universalteacher4u.com